Effects of Cross-Ridge Phase q = kL | |
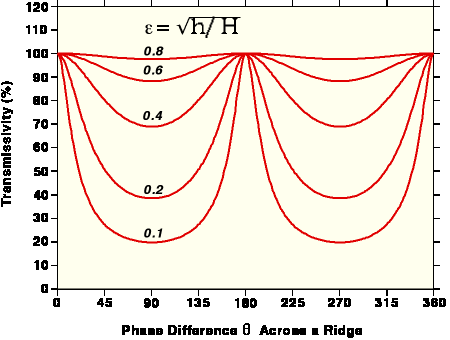 |
Minimum transmission (Tmin) occurs when q = 90°, 270°, 450°,... 100% transmission occurs when the cross-ridge phase shift q = kL is exactly q = 180°, 360°,... |
Effects of Cross-Ridge Phase q = kL | |
 |
Minimum transmission (Tmin) occurs when q = 90°, 270°, 450°,... 100% transmission occurs when the cross-ridge phase shift q = kL is exactly q = 180°, 360°,... |